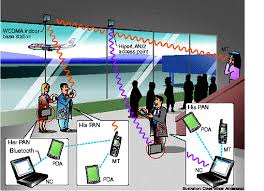
Personal area network
A personal area network (PAN) is a computer network used for communication among computer and different information technological devices close to one person. Some examples of devices that are used in a PAN are personal computers, printers, fax machines, telephones, PDAs, scanners, and even video game consoles. A PAN may include wired and wireless devices. The reach of a PAN typically extends to 10 meters. A wired PAN is usually constructed with USB and Firewire connections while technologies such as Bluetooth and infrared communication typically form a wireless PAN.
Local area network
A local area network (LAN) is a network that connects computers and devices in a limited geographical area such as home, school, computer laboratory, office building, or closely positioned group of buildings. Each computer or device on the network is a node. Current wired LANs are most likely to be based on Ethernet technology, although new standards like ITU-T G.hn also provide a way to create a wired LAN using existing home wires (coaxial cables, phone lines and power lines).
All interconnected devices must understand the network layer (layer 3), because they are handling multiple subnets (the different colors). Those inside the library, which have only 10/100 Mbit/s Ethernet connections to the user device and a Gigabit Ethernet connection to the central router, could be called "layer 3 switches" because they only have Ethernet interfaces and must understand IP. It would be more correct to call them access routers, where the router at the top is a distribution router that connects to the Internet and academic networks' customer access routers.
The defining characteristics of LANs, in contrast to WANs (Wide Area Networks), include their higher data transfer rates, smaller geographic range, and no need for leased telecommunication lines. Current Ethernet or other IEEE 802.3 LAN technologies operate at speeds up to 10 Gbit/s. This is the data transfer rate. IEEE has projects investigating the standardization of 40 and 100 Gbit/s. LANs can be connected to Wide area network by using routers.
Home network
A home network is a residential LAN which is used for communication between digital devices typically deployed in the home, usually a small number of personal computers and accessories, such as printers and mobile computing devices. An important function is the sharing of Internet access, often a broadband service through a cable TV or Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) provider.
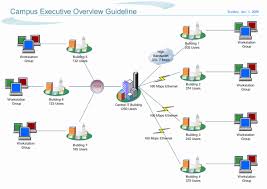
Campus network
A campus network is a computer network made up of an interconnection of LANs within a limited geographical area. The networking equipment (switches, routers) and transmission media (optical fiber, copper plant, Cat5 cabling etc.) are almost entirely owned (by the campus tenant / owner: an enterprise, university, government etc.).
In the case of a university campus-based campus network, the network is likely to link a variety of campus buildings including, for example, academic colleges or departments, the university library, and student residence halls
Backbone network
A backbone network is part of a computer network infrastructure that interconnects various pieces of network, providing a path for the exchange of information between different LANs or subnetworks. A backbone can tie together diverse networks in the same building, in different buildings in a campus environment, or over wide areas. Normally, the backbone's capacity is greater than that of the networks connected to it.
A large corporation which has many locations may have a backbone network that ties all of these locations together, for example, if a server cluster needs to be accessed by different departments of a company which are located at different geographical locations. The equipment which ties these departments together constitute the network backbone. Network performance management including network congestion are critical parameters taken into account when designing a network backbone.
A specific case of a backbone network is the Internet backbone, which is the set of wide-area network connections and core routers that interconnect all networks connected to the Internet.
Metropolitan area network
A Metropolitan area network (MAN) is a large computer network that usually spans a city or a large campus.
A metropolitan area network (MAN) is a network that interconnects users with computer resources in a geographic area or region larger than that covered by even a large local area network (LAN) but smaller than the area covered by a wide area network (WAN). The term is applied to the interconnection of networks in a city into a single larger network (which may then also offer efficient connection to a wide area network). It is also used to mean the interconnection of several local area networks by bridging them with backbone lines. The latter usage is also sometimes referred to as a campus network.
Examples of metropolitan area networks of various sizes can be found in the metropolitan areas of London, England; Lodz, Poland; and Geneva, Switzerland. Large universities also sometimes use the term to describe their networks. A recent trend is the installation of wireless MANs.
Wide area network
A wide area network (WAN) is a computer network that covers a large geographic area such as a city, country, or spans even intercontinental distances, using a communications channel that combines many types of media such as telephone lines, cables, and air waves. A WAN often uses transmission facilities provided by common carriers, such as telephone companies. WAN technologies generally function at the lower three layers of the OSI reference model: the physical layer, the data link layer, and the network layer.
Enterprise private network
An enterprise private network is a network built by an enterprise to interconnect various company sites, e.g., production sites, head offices, remote offices, shops, in order to share computer resources.
Virtual private network:
A virtual private network (VPN) is a computer network in which some of the links between nodes are carried by open connections or virtual circuits in some larger network (e.g., the Internet) instead of by physical wires. The data link layer protocols of the virtual network are said to be tunneled through the larger network when this is the case. One common application is secure communications through the public Internet, but a VPN need not have explicit security features, such as authentication or content encryption. VPNs, for example, can be used to separate the traffic of different user communities over an underlying network with strong security features.
VPN may have best-effort performance, or may have a defined service level agreement (SLA) between the VPN customer and the VPN service provider. Generally, a VPN has a topology more complex than point-to-point.
Internetwork
An internet work is the connection of multiple computer networks via a common routing technology using routers. The Internet is an aggregation of many connected internet works spanning the Earth.